Strength Training: Why it is Important for Moms
NOV 05, 2025Progressive overload means consistently challenging your muscles to do a little bit more than they're used to.
Read More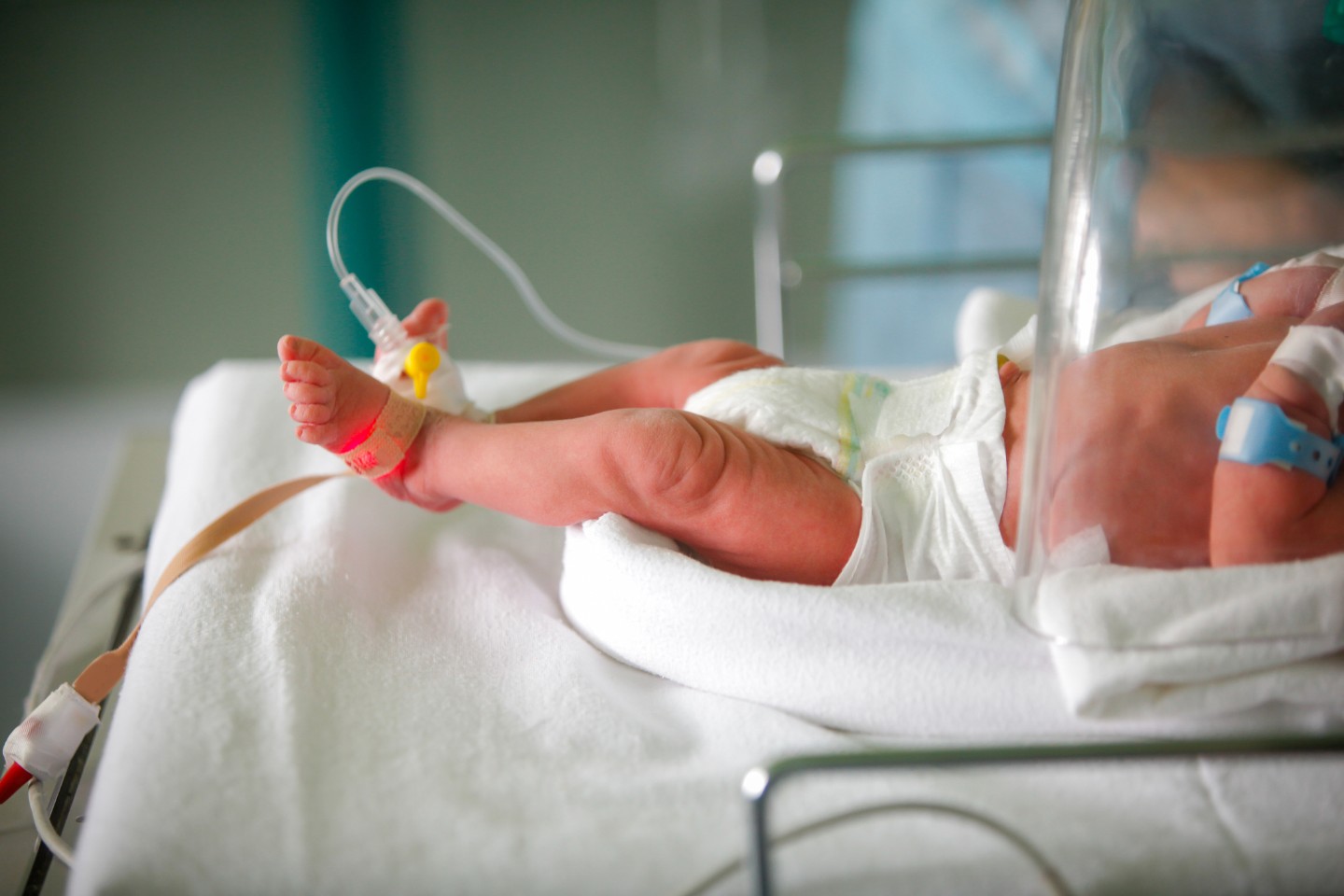
As eager as expectant parents are for the big day to arrive, they know it shouldn’t come too soon. Preterm births are quite common, with about 1 in 10 babies worldwide born before 37 weeks of pregnancy.
Because the health of the baby is the top concern for expectant parents, this topic can spark concern and anxiety. Sharing the facts about preterm and premature birth can help shine a helpful light on this important topic.
“Preterm” refers to the gestational age of babies born before the 37th week. “Premature” is the term used for both the gestational age and the potential health risks associated with being born before 37 weeks. Put simply, “premature” describes a baby born before it is fully developed who may require additional medical care. “Preterm” simply refers to the gestational age.
While babies grow and develop throughout pregnancy, the final weeks are when the brain, lungs and liver fully develop. Delivery is not scheduled before 39 weeks unless there is a medical need because higher rates of death and disability occur when babies are born too early – especially before 32 weeks. Potential complications include:
Many factors contribute to premature birth, and some are beyond our control. Genetic predisposition, certain medical conditions and even environmental factors can play a role.
Women who use an assisted reproductive technology (ART) such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) are at higher risk for preterm birth, primarily due to carrying multiples such as twins or triplets.
The risk of premature births can be reduced through proper prenatal care, healthy lifestyle choices, and early detection of potential risks. Important steps to take include:
It’s important to emphasize that we often simply don’t know what causes one woman to deliver early, and another woman carry to the full 40 weeks. Research has identified some demographic and social characteristics related to preterm birth. These include:
It may be surprising to learn that not all preterm babies are tiny and/or sick. The size and health of a premature baby depend on the gestational age at birth and other factors. While premature babies do face an increased risk of health challenges, medical advances have significantly improved the survival rates and long-term health outcomes.
The severity of potential complications depends on the gestational age at birth and the baby's health. Some babies may only need a few days of care in a NICU, while others may require weeks or even months.
The goal is to provide the necessary support and care for each premature baby to reach their full potential.
The importance of prenatal care throughout pregnancy can not be overemphasized. If you have any concerns before or during pregnancy, talk to your provider. Together, we can take important steps to protect the health of your baby.
Resources:

Progressive overload means consistently challenging your muscles to do a little bit more than they're used to.
Read More
Miscarriage, stillbirth, and infant loss are not merely medical events; they represent deeply personal tragedies that leave lasting imprints.
Read More
Meningitis is the inflammation of the membranes (meninges) that surround and protect the brain and spinal cord.
Read MoreWhen you need local health information from a trusted source, turn to the CHI Health Better You eNewsletter.