Fueling Your Family's Future: A Doctor's Perspective on National Nutrition Month
MAR 01, 2026Good nutrition is about building a foundation for a vibrant, energetic, and disease-resistant life for you and your loved ones.
Read More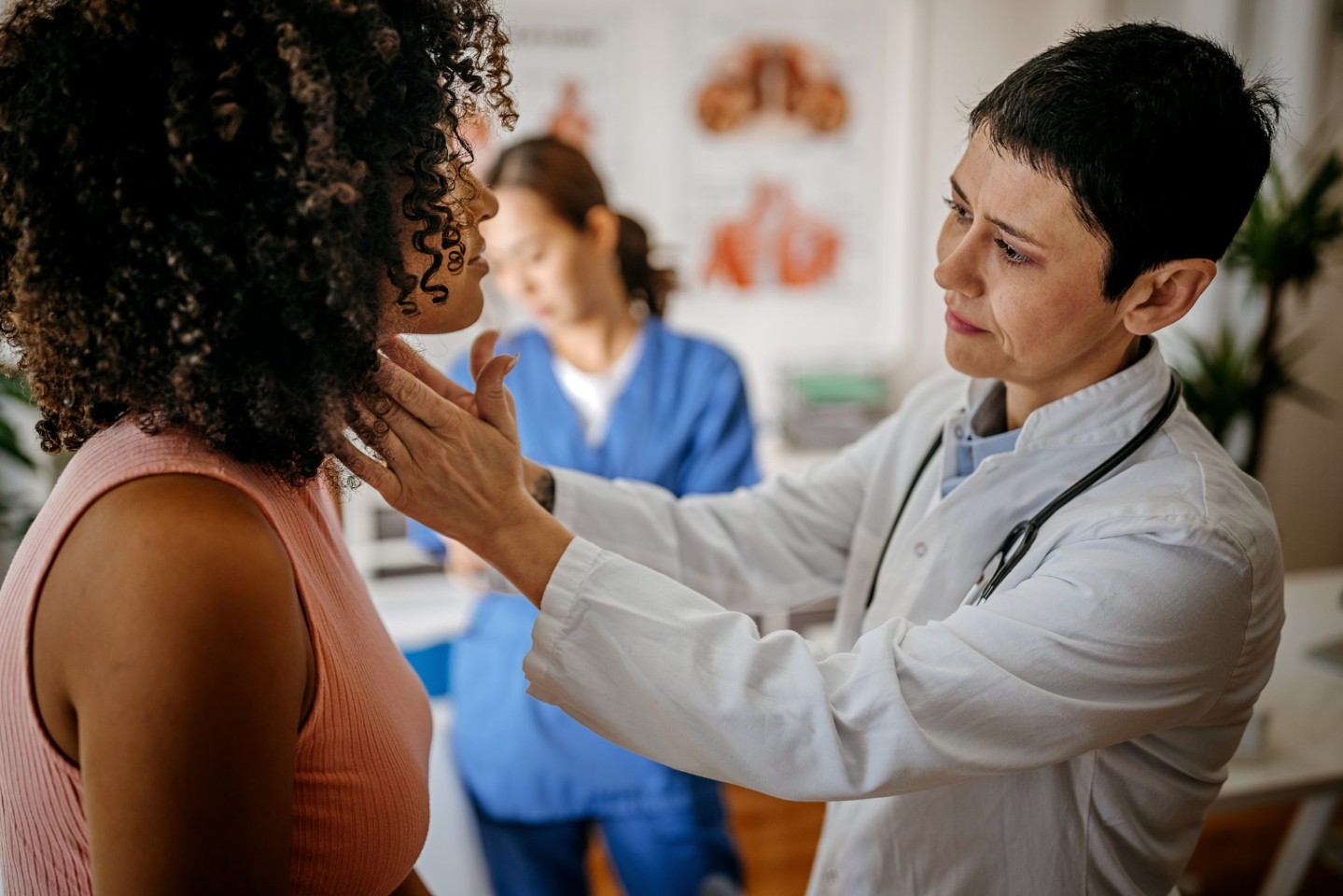
You probably don’t give your thyroid much thought. This quarter-sized gland just below your Adam’s apple secretes hormones that moderate your metabolism, heart rate, mood -- and more. It works quietly in the background, until something goes wrong.
One in 10 people worldwide have thyroid disease, and it affects women more often than men. The most common cause is Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune disorder. Grave’s disease can also affect the thyroid, as can side effects of medications, excess or inadequate iodine or other problems with your thyroid gland.
Fatigue and hair thinning are the most common symptoms of thyroid disease I see in my practice, but there are others. In fact, the symptoms are nearly opposite for an underactive versus an overactive thyroid. Both hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can present with an enlarged thyroid.
Diagnosing thyroid disease generally takes a simple blood test to check your hormone levels for an underactive or overactive thyroid.
Treatments for hypothyroidism are effective and individualized to you. For hypothyroidism, we typically start a dose of a thyroid medication to see if it helps with symptoms. If you are older, we may start with a lower dose. This decision is based on symptoms. We want to make sure you are feeling better on the medication, so we will have you come back after six weeks to get repeat TSH and T4 levels -- and adjust your medication up or down accordingly.
Treatment for hyperthyroidism is more varied and includes beta blockers to lower heart rate, medications to reduce thyroid hormone levels, radioiodine injection to slow down thyroid production or surgical removal of part of the thyroid.
Diagnosing and treating thyroid disease is important because untreated thyroid problems can lead to other conditions, including heart problems, obesity, joint pain and infertility. If you have symptoms or questions, contact your primary care provider.

Good nutrition is about building a foundation for a vibrant, energetic, and disease-resistant life for you and your loved ones.
Read More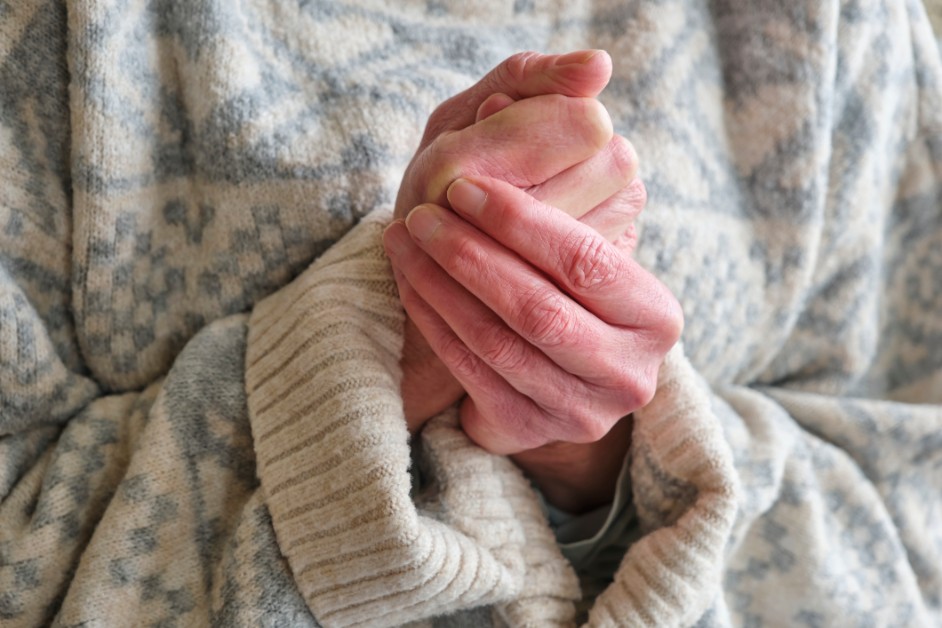
Raynaud's phenomenon is a rare disorder that affects the blood vessels, most commonly in the fingers and toes, but sometimes also in the nose, ears, or lips.
Read More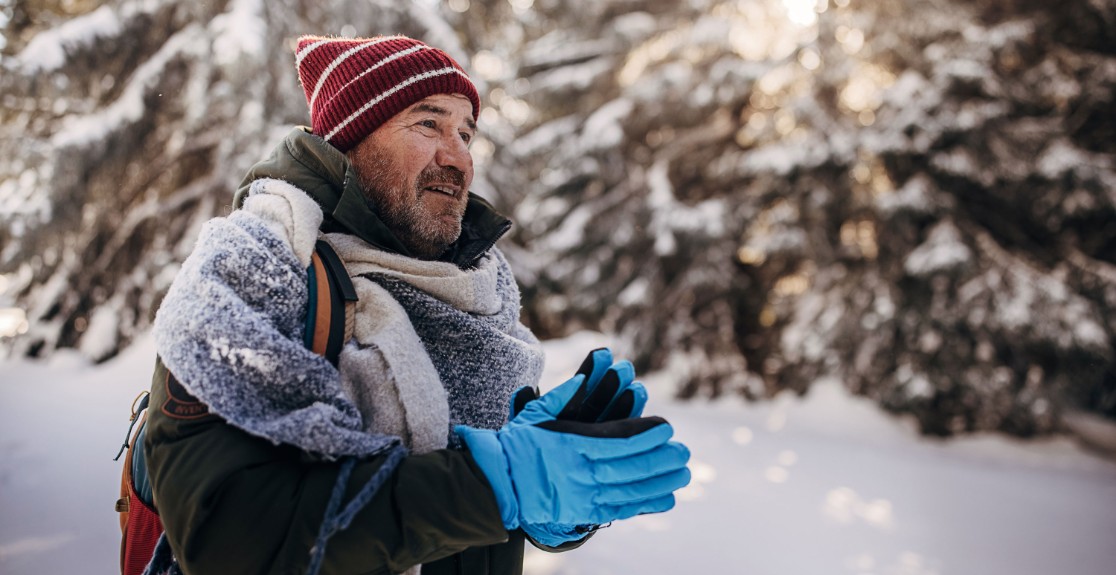
Winter brings beautiful snowy landscapes and cozy evenings, but the cold, dry air—indoors and out—can be harsh on our hands, leading to dryness, cracking, and even more serious issues like frostbite. Protecting your hands is crucial for comfort and s...
Read MoreWhen you need local health information from a trusted source, turn to the CHI Health Better You eNewsletter.